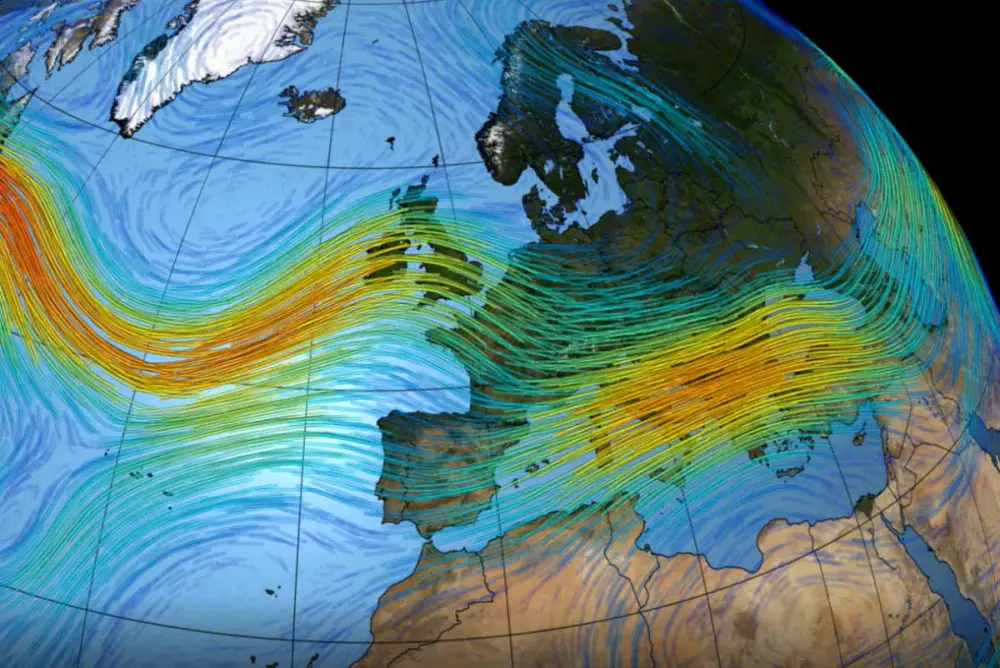
Shifting North Atlantic Jet Stream Could Increase Extreme Weather in Europe by 2060
With rising global temperatures, the world is seeing a drastic change in climatic patterns. A report has stated that shifting the North Atlantic jet stream could increase extreme weather events in Europe and North America by 2060.
The North Atlantic jet stream is a band of predominant, westerly winds that encircle the Arctic and give a lift to aircraft flying from the US to Europe. While the jet stream blows toughest at airliner cruising altitudes, it also reaches down to the ground and acts significantly in local weather conditions.
Published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, experts led from the University of Arizona took samples of ice from Greenland ice sheets to extract a record of past weather. The researchers studied how the layers of snow were deposited over the last 1,250 years.
About 10-15 percent of the variation in annual precipitation and temperature in eastern North American and West Europe originates from the jet stream.
The study also pointed out that this year’s heatwave in the Pacific Northwest and the floods that hit Europe are a few instances of how jet stream disparities can influence the weather.
From the collected data, the researchers reconstructed the past locations and intensities of the jet stream. They discovered that climate change has not pushed it past its natural changeability yet.
According to the paper author and climate scientist Matthew Osman of the University of Arizona;
What we do know is that extraordinary variations in the jet stream can have severe societal implications — such as floods and droughts — due to its impacts on weather patterns. So, in terms of thinking about the future, we can now begin to use the past as a sort of prologue.
The projections of the study suggest that usual greenhouse emissions will nudge the jet stream northwards, leading to drastic changes in a couple of decades.
Analyzing the natural records, the team was able to recreate changes in windiness across the North Atlantic on an annual basis going back to the 8th –century. They found that the fluctuations in the jet stream’s intensity and position are within the limits of natural dissimilarity.
However, the study concluded that if global warming continues at the current rate, drastic changes will manifest within a matter of decades, with the jet stream expected to migrate its average position northwards.
These variations have huge implications on the weather experienced at a given place. The team did find evidence of societal importance changes in the jet stream’s history, sometimes drifting north. The results serve as a warning.
Via: Daily Milk